ASA PRE OPERATIVE RECOMMENDATIONS MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
7 Myocardial infarction MI or injury perioperatively increases the risk of death. With the announcement by the Royal College of Anaesthetists of the National Audit Programme 7 NAP7 on perioperative cardiac arrest it is opportune to examine the management of early perioperative ST-elevation myocardial infarction STEMI a life-threatening adverse event.

Med Life Easy Pg Preparation On Instagram Myocardial Infarction Follow Me Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical Surgical Nursing Respiratory Therapy Student
Patients at low risk for perioperative cardiovascular events are those taking antiplatelet therapy for primary prevention of MI or stroke although this is rarely indicated.
. Myocardial ischemia is a major complication in the perioperative period mostly in patients with high cardiac risks. 3 Brief recommendations are made for a patient suffering a perioperative MI. These include consideration for prompt angioplasty aspirin beta-blockade and possible angiotensin.
The propensity of myocardial injury is dictated by the conglomeration of various factors like pre-existing medical condition high-risk surgical interventions intraoperative hemodynamic management and the postoperative care. Nonfatal myocardial infarction cardiogenic shock. Myocardial ischemia with or without subsequent myocardial infarction MI is a common and feared cardiac complication of noncardiac surgery with an inpatient mortality in the range of 5-17.
Perioperative myocardial infarction PMI differs from myocardial infarction MI in a non-operative setting. Need for noncardiac surgery Urgent or elective. Continue aspirin and discontinue clopidegrol 5 days before surgery if intermediate risk of bleeding or continue clopidegrol as well minor risk of bleeding.
2022 American Society of Anesthesiologists Practice Guidelines for Management of the Difficult Airway. 1-3 Noncardiac surgery is associated with platelet activation 4 and coronary-artery. Recommendations for the perioperative man-.
The focus of the evaluation has been on identifying baseline comorbidities that will lead to modification of perioperative care. Should a myocardial infarction MI occur the mortality rate remains at 40 to 70. 16 17 12 Perioperative MI PMI is the most common of the cardiac complications causing postoperative morbidity and mortality.
From information in American Society of Anesthesiologists 11. Attempts to improve perioperative outcome of patients at risk for having CAD have focused on 3 approaches. Myocardial injury is a common postoperative vascular complication.
Myocardial infarction is the most common major vascular complication that occurs after noncardiac surgery. And preoperative ces-sation of. Patients at low risk for perioperative cardiovascular events are those taking antiplatelet therapy for primary prevention of MI or stroke although this is rarely indicated.
A major concern after successful coronary artery stent placement is the potential for acute stent thrombosis with subsequent myocardial infarction and death1 To. Patients who suffer PMI may on average incur an additional 10000 - 20000 in additional hospital costs. 20181 and also guidelines on myocardial revascularisation from the European Society of Cardiology and European As-sociation Cardiothoracic Surgery 20182 Yet there is no consensus on the management of STEMI in the perioperative setting.
History of prior myocardial infarction ASA Class 4 Severe systemic disturbance that is life-threatening with or. With respect to specific medical conditions the evaluation of the patient with cardiac disease was one of the earliest focuses. Genetic Variation β-blockers and Perioperative Myocardial Infarction.
Noncardiac surgery administration of perioperative aspirin would prevent 59 myocardial infarctions CI 10 to 108 myocardial infarctions and cause 8 major bleeding On the basis of this studys findings 17 patients with prior PCI 95 CI 9 to 100 patients would need to be treated with aspirin to prevent 1 myocardial infarction during the perioperative period the editorialists. Perioperative myocardial infarction and death in these patients and 2 the relation between antiplatelet ther-apy and acute perioperative stent thrombosis. The classification system alone does not predict the perioperative risks but used with other factors eg type of surgery frailty level of deconditioning.
The purpose of the system is to assess and communicate a patients pre-anesthesia medical co-morbidities. If the patient is planned for other surgeries. Perioperative STEMI Perioperative myocardial infarction PMI is an uncommon and life-threatening event.
A Report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists Task Force on Moderate Procedural Sedation and Analgesia. Recent myocardial infarction MI those with carotid ulcerating plaque and stroke or aortic ulcerating plaque and systemic embolism. Stop aspirin and clopidegrol 5 days before surgery.
1 in 10 patients dies within 30 days after surgery. Perioperative myocardial infarction PMI may be lethal or compromise a patients functional status after surgery. Recent myocardial infarction MI or those with carotid ulcerating plaque and stroke.
If the patient is planned for high bleeding risk surgery. Long-term antiplatelet therapy is an important component of secondary prevention after a stroke myocardial infarction MI myocardial revascularization or a diagnosis of peripheral arterial. Clinicians must balance these risks.
With pharmacological and technical developments in coronary reperfusion over recent. Recommendations and Guidelines For Preoperative Evaluation Of the Surgical Patient. The ASA Physical Status Classification System has been in use for over 60 years.
Surgery creates substantial physiologic stress through factors such as fasting anesthesia intubation surgical trauma extubation and pain. The authors recognize that perioperative cardiovascular morbidity and modalities can never be entirely eliminated. After non-cardiac surgery myocardial infarction was observed in 56 of patients with coronary heart disease the rate in patients with no cardiac diseases was 01-07.
THE preoperative evaluation of the patient has been a key function of anesthesiologists.
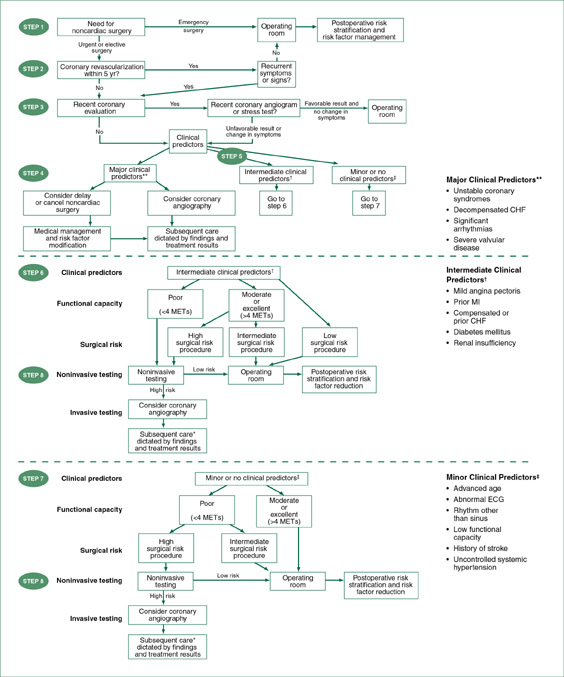
Acc Aha Updates Preoperative Cardiac Guidelines Anesthesia Patient Safety Foundation

Myocardial Infarction Interventions Myocardial Infarction For Nursing Rn

Acute Myocardial Infarction Nejm

Study Design Asa Indicates Aspirin Iv Intravenous Pd Download Scientific Diagram

Supplemental Materials For Myocardial Infarction After Noncardiac Surgery In Sweden A National Retrospective Observational Cohort Study British Journal Of Anaesthesia

Supplemental Materials For Canadian Cardiovascular Society Guidelines On Perioperative Cardiac Risk Assessment And Management For Patients Who Undergo Noncardiac Surgery Canadian Journal Of Cardiology

Acls Algorithm Overview Acls Acute Coronary Syndrome Nursing School Pharmacology
0 Response to "ASA PRE OPERATIVE RECOMMENDATIONS MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION"
Post a Comment